-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Features Inspector Inspector Validation Attributes
Protect your data with declarative validation and read-only presentation.
Unity Helpers provides validation attributes that help maintain data integrity and prevent accidental modifications. These attributes work seamlessly with the Unity inspector and can validate fields at runtime.
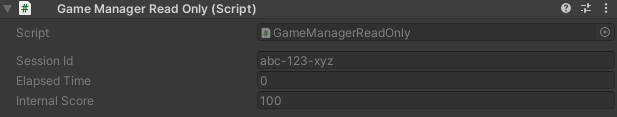
Displays a field in the inspector as read-only, preventing accidental modifications while keeping the value visible.
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class GameManagerReadOnly : MonoBehaviour
{
[WReadOnly]
public string sessionId = "abc-123-xyz";
[WReadOnly]
public float elapsedTime = 0f;
[WReadOnly]
[SerializeField]
private int internalScore = 100;
}Behavior:
- Field appears grayed out in the inspector
- Value is visible but cannot be edited through the inspector
- Useful for displaying computed values, debug info, or auto-generated IDs
- Works with any serializable field type
Visual Reference
Fields marked with [WReadOnly] appear grayed out and cannot be edited
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class EntityReadOnly : MonoBehaviour
{
// Auto-generated unique identifier
[WReadOnly]
public string entityId = System.Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
// Computed property exposed for debugging
[WReadOnly]
[SerializeField]
private float _currentHealth;
// Reference that should only be set via code
[WReadOnly]
public Transform cachedTarget;
// Frame counter for debugging
[WReadOnly]
public int framesSinceLastUpdate;
}Why Use WReadOnly:
- Prevent accidents: Stop designers from accidentally modifying auto-generated values
- Debug visibility: Show internal state without allowing modification
- Documentation: Make it clear which fields are managed by code vs. configured in the editor
- Data integrity: Protect computed or cached values from manual overrides
Visual Reference
Multiple field types (string, float, Transform, int) displayed as read-only
Validates that a field is not null, providing both visual inspector feedback and runtime validation. When a field marked with [WNotNull] is null, the inspector displays a warning or error HelpBox. Additionally, calling CheckForNulls() on an object will throw an ArgumentNullException for any null [WNotNull] fields.
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class PlayerControllerNotNull : MonoBehaviour
{
[WNotNull]
public Rigidbody2D rb;
[WNotNull]
public SpriteRenderer spriteRenderer;
[WNotNull]
[SerializeField]
private AudioSource audioSource;
private void Awake()
{
// Validates all [WNotNull] fields are assigned
// Throws ArgumentNullException if any are null in Editor ONLY
this.CheckForNulls();
}
}Behavior:
- Inspector feedback: Displays a HelpBox warning (yellow) or error (red) when the field is null
-
Runtime validation: Call
this.CheckForNulls()to validate all[WNotNull]fields - Throws
ArgumentNullExceptionwith the field name if any marked field is null - Works with both Unity
Objecttypes and plain C# objects - All validation runs only in the Unity Editor (stripped in builds for performance)
Visual Reference
Fields marked with [WNotNull] display a HelpBox in the inspector when null
The WNotNullMessageType enum controls how null fields are displayed in the inspector:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
Warning |
Displays a yellow warning HelpBox (default) |
Error |
Displays a red error HelpBox |
The [WNotNull] attribute supports multiple constructor overloads for flexibility:
// Default: warning message type with auto-generated message
[WNotNull]
public GameObject target;
// Inspector shows: "target must be assigned"// Error message type with auto-generated message
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error)]
public AudioSource criticalAudioSource;
// Inspector shows red error: "criticalAudioSource must be assigned"// Warning with custom message
[WNotNull("Player needs a target to attack")]
public Transform attackTarget;
// Inspector shows yellow warning: "Player needs a target to attack"// Error with custom message
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error, "Audio source is required for sound effects")]
public AudioSource audioSource;
// Inspector shows red error: "Audio source is required for sound effects"using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class EnemyAI : MonoBehaviour
{
// Yellow warning - nice to have
[WNotNull]
public ParticleSystem hitEffect;
// Red error - critical reference
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error)]
public Transform patrolPath;
// Warning with helpful context
[WNotNull("Assign the player tag or the enemy won't detect the player")]
public string playerTag;
// Error with specific instructions
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error, "Drag the NavMeshAgent component here - required for movement")]
public UnityEngine.AI.NavMeshAgent agent;
}Visual Reference
Warning (yellow) and Error (red) HelpBoxes for null fields in the inspector
The CheckForNulls() extension method validates all [WNotNull] fields at runtime:
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class EnemySpawner : MonoBehaviour
{
[WNotNull]
public GameObject enemyPrefab;
[WNotNull]
public Transform spawnPoint;
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error)]
public EnemyManager enemyManager;
private void Start()
{
// If any [WNotNull] field is null, this throws with the field name
// Example: ArgumentNullException("enemyPrefab")
this.CheckForNulls();
// Safe to use - we know these are assigned
SpawnEnemy();
}
private void SpawnEnemy()
{
GameObject enemy = Instantiate(enemyPrefab, spawnPoint.position, Quaternion.identity);
enemyManager.RegisterEnemy(enemy);
}
}Both the inspector HelpBox display and the CheckForNulls() extension method are only active in the Unity Editor:
// The validation code only runs in UNITY_EDITOR
// In builds, CheckForNulls() does nothing (stripped for performance)
this.CheckForNulls();This means:
- Development: Visual feedback in inspector + runtime null checking with detailed exception messages
- Production: Zero runtime cost (all validation code is stripped)
public class UIManager : MonoBehaviour
{
// Required reference with error severity - validated at runtime
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error)]
[SerializeField]
private Canvas mainCanvas;
// Optional reference - not validated
[SerializeField]
private AudioSource clickSound;
// Read-only and required
[WReadOnly]
[WNotNull]
public RectTransform cachedRect;
// Group with validation and custom message
[WGroup("UI Elements")]
[WNotNull("Start button required for main menu")]
public Button startButton; // In group
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error, "Quit button required for main menu")]
[WGroupEnd("UI Elements")] // quitButton IS included, then closes
public Button quitButton; // In group (last field)
}Why Use WNotNull:
- Visual feedback: See missing references immediately in the inspector without running the game
- Severity control: Use warnings for nice-to-have references, errors for critical ones
- Custom messages: Provide helpful context about why a reference is needed
-
Early failure: Catch missing references at game start with
CheckForNulls(), not when first used - Clear errors: Get the exact field name in the exception message
- Documentation: Make required references explicit in code
- Zero runtime cost: All validation stripped from builds
Validates that a field is properly assigned, providing visual inspector feedback when validation fails. Unlike [WNotNull] which only checks for null references, [ValidateAssignment] validates that fields are "properly assigned" based on their type—including checking for empty strings, empty collections, and null references.
| Field Type | Validation Rule |
|---|---|
Unity Object references |
Not null |
| Strings | Not null or whitespace |
IList (arrays, List)
|
Has at least one element |
ICollection |
Has at least one element |
IEnumerable |
Has at least one element |
| Other types | Not null |
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class EnemySpawner : MonoBehaviour
{
[ValidateAssignment]
public GameObject enemyPrefab;
[ValidateAssignment]
public string enemyName;
[ValidateAssignment]
public List<Transform> spawnPoints;
private void Start()
{
// Logs warnings for any invalid [ValidateAssignment] fields
this.ValidateAssignments();
}
}Behavior:
- Inspector feedback: Displays a HelpBox warning (yellow) or error (red) when the field is invalid
-
Runtime validation: Call
this.ValidateAssignments()to log warnings for invalid fields -
Programmatic checking: Call
this.AreAnyAssignmentsInvalid()to check if any fields are invalid - Works with Unity
Objecttypes, strings, collections, and any reference type - Inspector validation runs only in the Unity Editor (stripped in builds for performance)
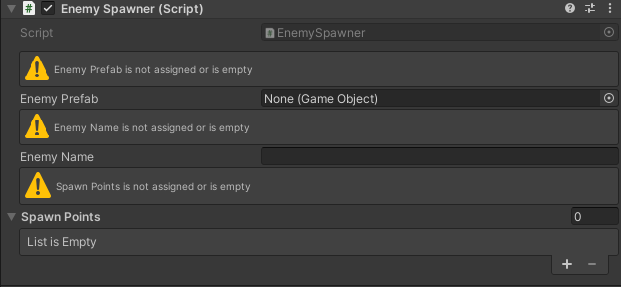
Visual Reference
Fields marked with [ValidateAssignment] display a HelpBox in the inspector when invalid
The ValidateAssignmentMessageType enum controls how invalid fields are displayed in the inspector:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
Warning |
Displays a yellow warning HelpBox (default) |
Error |
Displays a red error HelpBox |
The [ValidateAssignment] attribute supports multiple constructor overloads for flexibility:
// Default: warning message type with auto-generated message
[ValidateAssignment]
public GameObject target;
// Inspector shows: "target must be assigned"// Error message type with auto-generated message
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error)]
public AudioSource criticalAudioSource;
// Inspector shows red error: "criticalAudioSource must be assigned"// Warning with custom message
[ValidateAssignment("Enemy name is required for UI display")]
public string enemyName;
// Inspector shows yellow warning: "Enemy name is required for UI display"// Error with custom message
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error, "Spawn points list cannot be empty")]
public List<Transform> spawnPoints;
// Inspector shows red error: "Spawn points list cannot be empty"using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GameConfig : MonoBehaviour
{
// Yellow warning - validates not null
[ValidateAssignment]
public GameObject playerPrefab;
// Red error - validates string not empty/whitespace
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error)]
public string gameTitle;
// Warning with helpful context - validates list not empty
[ValidateAssignment("Add at least one difficulty level")]
public List<string> difficultyLevels;
// Error with specific instructions - validates array not empty
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error, "Spawn points are required - add Transform references")]
public Transform[] spawnPoints;
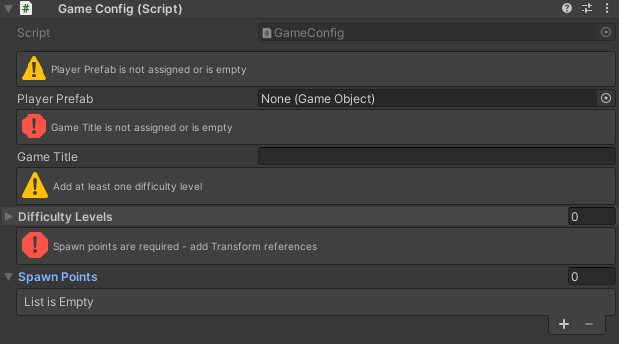
}Visual Reference
Warning (yellow) and Error (red) HelpBoxes for various invalid field types
Two extension methods are available for runtime validation of [ValidateAssignment] fields:
Logs warnings to the console for all invalid fields:
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class LevelManager : MonoBehaviour
{
[ValidateAssignment]
public GameObject[] enemyPrefabs;
[ValidateAssignment]
public string levelName;
private void Start()
{
// Logs a warning for each invalid [ValidateAssignment] field
this.ValidateAssignments();
}
}Returns true if any [ValidateAssignment] field is invalid:
using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
public class SpawnManager : MonoBehaviour
{
[ValidateAssignment]
public GameObject spawnPrefab;
[ValidateAssignment]
public List<Transform> spawnLocations;
private void Start()
{
if (this.AreAnyAssignmentsInvalid())
{
Debug.LogError("SpawnManager has invalid assignments - spawning disabled");
enabled = false;
return;
}
// Safe to proceed - all assignments are valid
SpawnEnemies();
}
}Both attributes validate fields and provide inspector feedback, but they serve different purposes:
| Feature | ValidateAssignment | WNotNull |
|---|---|---|
| Null object check | ✓ | ✓ |
| Empty string check | ✓ | ✗ |
| Empty collection check | ✓ | ✗ |
| Runtime behavior | Logs warnings | Throws ArgumentNullException
|
| Best for | Comprehensive field validation | Strict null reference checking |
When to use which:
- Use
[ValidateAssignment]when you need to validate that strings are non-empty or collections have elements - Use
[WNotNull]when you want strict null checking with an exception thrown at runtime - Use
[ValidateAssignment]when you want softer runtime validation (warnings instead of exceptions) - Use
[WNotNull]for critical references where the game should fail fast if not assigned
public class PlayerSetup : MonoBehaviour
{
// Use WNotNull for critical references - throws if null
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error)]
public Rigidbody2D rb;
// Use ValidateAssignment for string validation
[ValidateAssignment]
public string playerName;
// Use ValidateAssignment for collection validation
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error, "Add at least one weapon")]
public List<GameObject> startingWeapons;
private void Awake()
{
// Throws ArgumentNullException if rb is null
this.CheckForNulls();
// Logs warnings if playerName is empty or startingWeapons is empty
this.ValidateAssignments();
}
}using UnityEngine;
using WallstopStudios.UnityHelpers.Core.Attributes;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class UIManager : MonoBehaviour
{
// Group with validation
[WGroup("Required UI Elements")]
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error)]
public Canvas mainCanvas; // In group
[ValidateAssignment("Button text cannot be empty")]
public string startButtonText; // In group (auto-included)
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error, "Add menu items to display")]
[WGroupEnd("Required UI Elements")] // menuItems IS included, then closes
public List<GameObject> menuItems; // In group (last field)
// Conditional validation
[WShowIf(nameof(useCustomTheme))]
[ValidateAssignment("Custom theme name required when using custom theme")]
public string customThemeName;
public bool useCustomTheme;
}Why Use ValidateAssignment:
- Comprehensive validation: Validates strings, collections, and references—not just null checks
- Visual feedback: See invalid fields immediately in the inspector
- Severity control: Use warnings for nice-to-have fields, errors for critical ones
- Custom messages: Provide helpful context about validation requirements
-
Non-throwing validation: Use
ValidateAssignments()for warnings instead of exceptions -
Programmatic checking: Use
AreAnyAssignmentsInvalid()for conditional logic - Zero runtime cost: All validation stripped from builds
Call CheckForNulls() and ValidateAssignments() in Awake() or Start() to catch missing references immediately:
private void Awake()
{
// Throws for critical null references
this.CheckForNulls();
// Logs warnings for empty strings, collections, etc.
this.ValidateAssignments();
}// Use WNotNull for critical object references (throws on null)
[WNotNull(WNotNullMessageType.Error)]
public Rigidbody2D rb;
// Use ValidateAssignment for strings (validates not empty/whitespace)
[ValidateAssignment]
public string playerName;
// Use ValidateAssignment for collections (validates not empty)
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error)]
public List<Transform> waypoints;[WReadOnly]
public float Speed => rb.velocity.magnitude;// Auto-wired but protected from manual changes
[WReadOnly]
[SiblingComponent]
public Collider2D col;// Required: Must be assigned in inspector
[WNotNull]
public AudioClip attackSound;
// Required: Must not be empty
[ValidateAssignment]
public string characterName;
// Optional: May be null
public AudioClip hitSound;[CreateAssetMenu]
public class GameConfig : ScriptableObject
{
[WNotNull]
public GameObject playerPrefab;
[WNotNull]
public Material defaultMaterial;
[ValidateAssignment("Game title cannot be empty")]
public string gameTitle;
[ValidateAssignment(ValidateAssignmentMessageType.Error)]
public List<string> supportedLanguages;
private void OnEnable()
{
this.CheckForNulls();
this.ValidateAssignments();
}
}- Inspector Grouping Attributes - Organize related fields
- Inspector Conditional Display - Show/hide fields conditionally
- Relational Components - Auto-wire component references
📦 Unity Helpers | 📖 Documentation | 🐛 Issues | 📜 MIT License
- Inspector Button
- Inspector Conditional Display
- Inspector Grouping Attributes
- Inspector Inline Editor
- Inspector Overview
- Inspector Selection Attributes
- Inspector Settings
- Inspector Validation Attributes
- Utility Components
- Visual Components
- Data Structures
- Helper Utilities
- Math And Extensions
- Pooling Guide
- Random Generators
- Reflection Helpers
- Singletons