-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 3
Neural Networks
Artificial Neural Networks are the biologically inspired simulations performed on the computer to perform certain specific tasks like clustering, classification, pattern recognition etc.
Artificial Neural Networks, in general — is a biologically inspired network of artificial neurons configured to perform specific tasks.
There are 4 main types of artificial neural network learning algorithms: supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement and deep learning.
Artificial neural networks can be viewed as weighted directed graphs in which artificial neurons are nodes and directed edges with weights are connections between neuron outputs and neuron inputs.
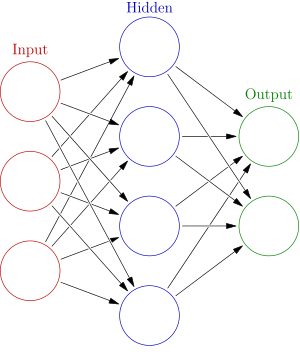
A typical neural network contains a large number of artificial neurons called units arranged in a series of layers. In typical artificial neural network, comprises different layers -
Input layer — It contains those units (artificial neurons) which receive input from the outside world on which network will learn, recognize about or otherwise process.
Output layer — It contains units that respond to the information about how it’s learned any task.
Hidden layer — These units are in between input and output layers. The job of hidden layer is to transform the input into something that output unit can use in some way.
Most neural networks are fully connected that means to say each hidden neuron is fully connected to the every neuron in its previous layer(input) and to the next layer (output) layer.
The Artificial Neural Network receives various inputs. Each input is multiplied by its corresponding weights. Weights are the information used by the neural network to solve a problem. Typically weight represents the strength of the interconnection between neurons inside the neural network. A high weighting indicates that a particular neuron connection has a significant effect on the output of the network.
The weighted inputs are all summed up inside computing unit (artificial neuron) as well as a constant referred to as bias. This is similar to the linear regression model (see supervised learning chapter) which uses a line equation to make classifications.
The sum corresponds to any numerical value ranging from 0 to infinity. We pass this value to an activation function.
The weighted sum of the inputs produces the activation signal that is passed to the activation function to obtain one output from the neuron. The commonly used activation functions are linear, step, sigmoid, tanh, and rectified linear unit (ReLu) functions.
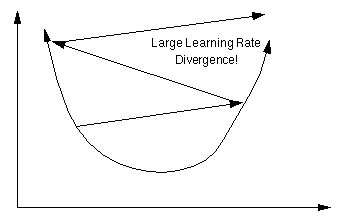
So now that we have a neural network that is assigning these weightings and making classifications/regressions how do we train it to perform well?
Backpropagation is a method used in artificial neural networks to calculate the error contribution of each neuron after a batch of data is processed. This is commonly implemented in the gradient descent optimization algorithm to adjust the weight of neurons by calculating the gradient of the loss function. This technique is also sometimes called backward propagation of errors, because the error is calculated at the output and distributed back through the network layers.
https://deeplearning4j.org/img/updater_animation2.gif